Exploring Leather’s : Origins, Types, and Modern Applications
Introduction
Leather has charmed people for a long term, serving as both a realistic fabric and a image of luxury. What is it approximately leather that keeps attractive us? How has this flexible material developed throughout the long term, and what are today applications? This article digs into the interesting universe of leather, investigating its rich history, the specialty of leathercraft, and its current importance.
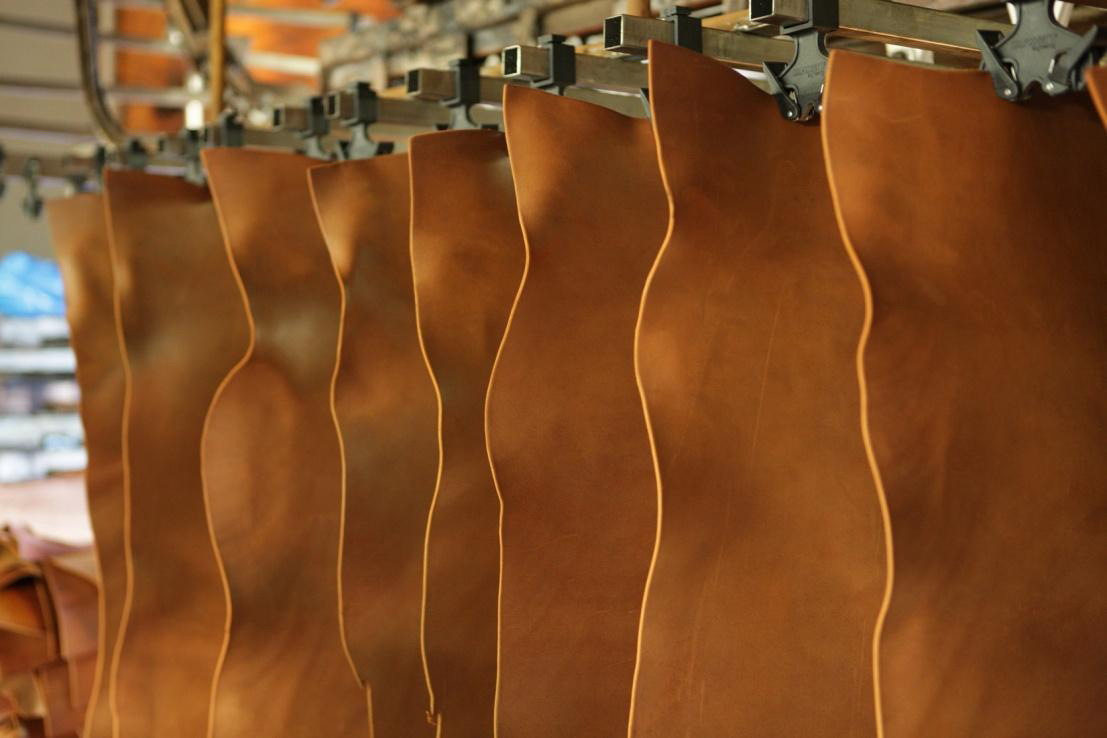

1. The Rich History of Leather
Leather’s story starts in antiquated times, with proof of its utilization tracing all the way back to ancient periods. Early people perceived the strength and flexibility of creature stows away, involving them for dress, haven, and devices. After some time, individuals grew more modern procedures for tanning and protecting leather, prompting the making of leather merchandise that were both utilitarian and beautifying.
The Ancient World and Leather: In old Egypt, individuals involved leather for shoes, gloves, and even reinforcement. The Egyptians culminated tanning strategies that delivered graceful and sturdy leather. Furthermore, the Greeks and Romans valued leather for its energy and flexibility, the usage of it for shoes, protecting tools, and saddles.
Medieval Europe: Throughout the Middle Ages, leather-based became a commonplace fabric in Europe. Tanners, or craftsmen, organized guilds to protect and promote their trade. People utilized leather for everyday objects like belts, bags, and books. The development of bookbinding elevated leather to the status of art, with beautifully tooled covers protecting important manuscripts.
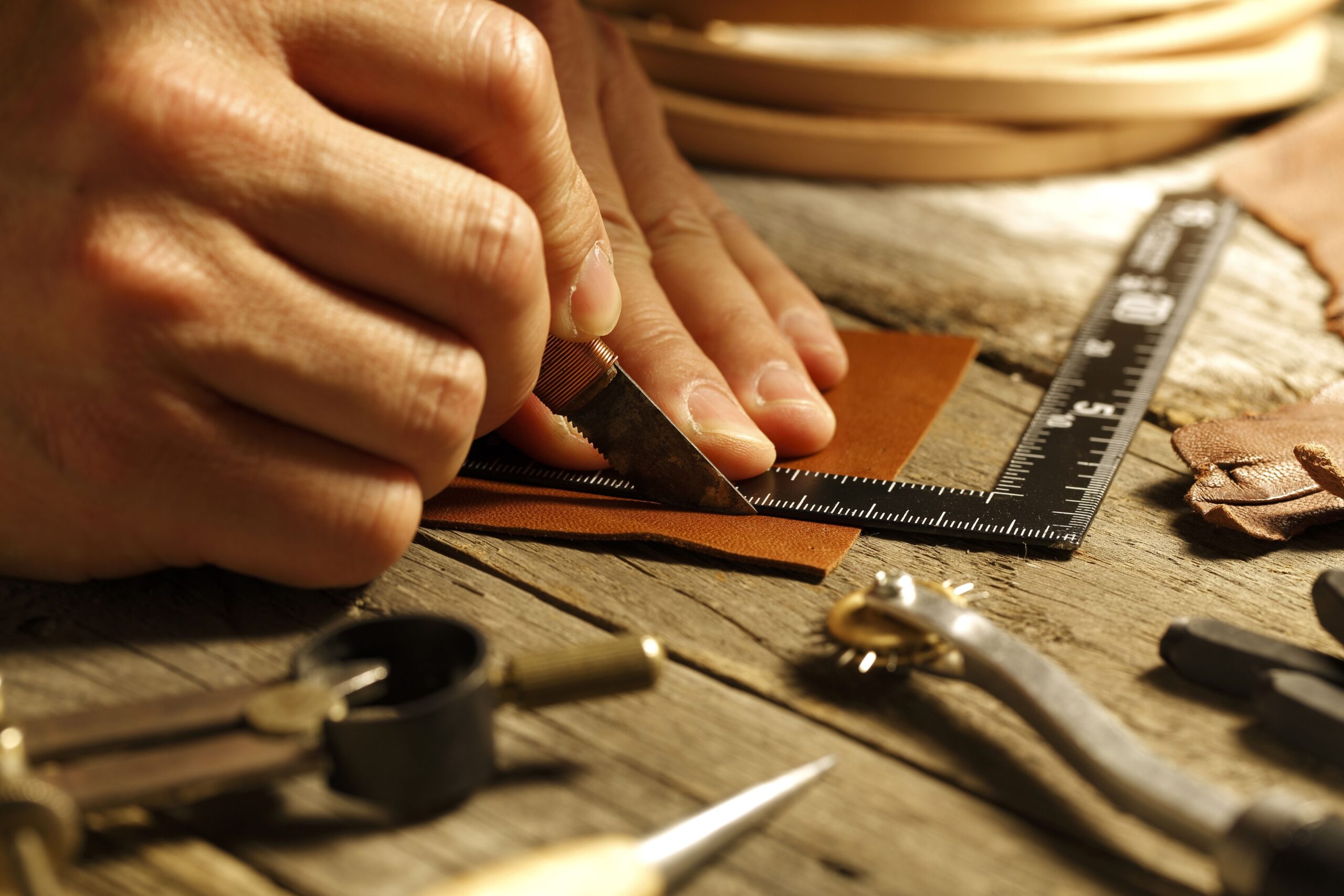

2. The Art and Craft of Leatherwork
Leatherworking is an ancient craft that demands expertise, precision, and inventiveness. The transformation of raw skins into completed leather-based items is a multi-step manner, each of which is crucial to the end product’s pleasant.
Tanning: The tanning procedure keeps up with the camouflage and holds it back from debasing. There are different tanning draws near, including vegetable tanning, which utilizes regular plant tannins, and chrome tanning, which utilizes chromium salts. Every methodology gives exact characteristics to the leather based, influencing its shade, surface, and strength.
Cutting and Shaping: When tanned, the leather based is ready to be cut and molded. Experts utilize examples to diminish and join parts together, which expects accuracy to make an ideal suit and to complement the leather’s intrinsic grain.
Sewing and Finishing: Sewing interfaces the leather parts to make the completed item. Experts can entire this activity by utilizing hand or device, with hand-sewing frequently viewed as an indication of top notch craftsmanship. Cleaning, shading, and joining equipment complete the leather’s appearance and execution.
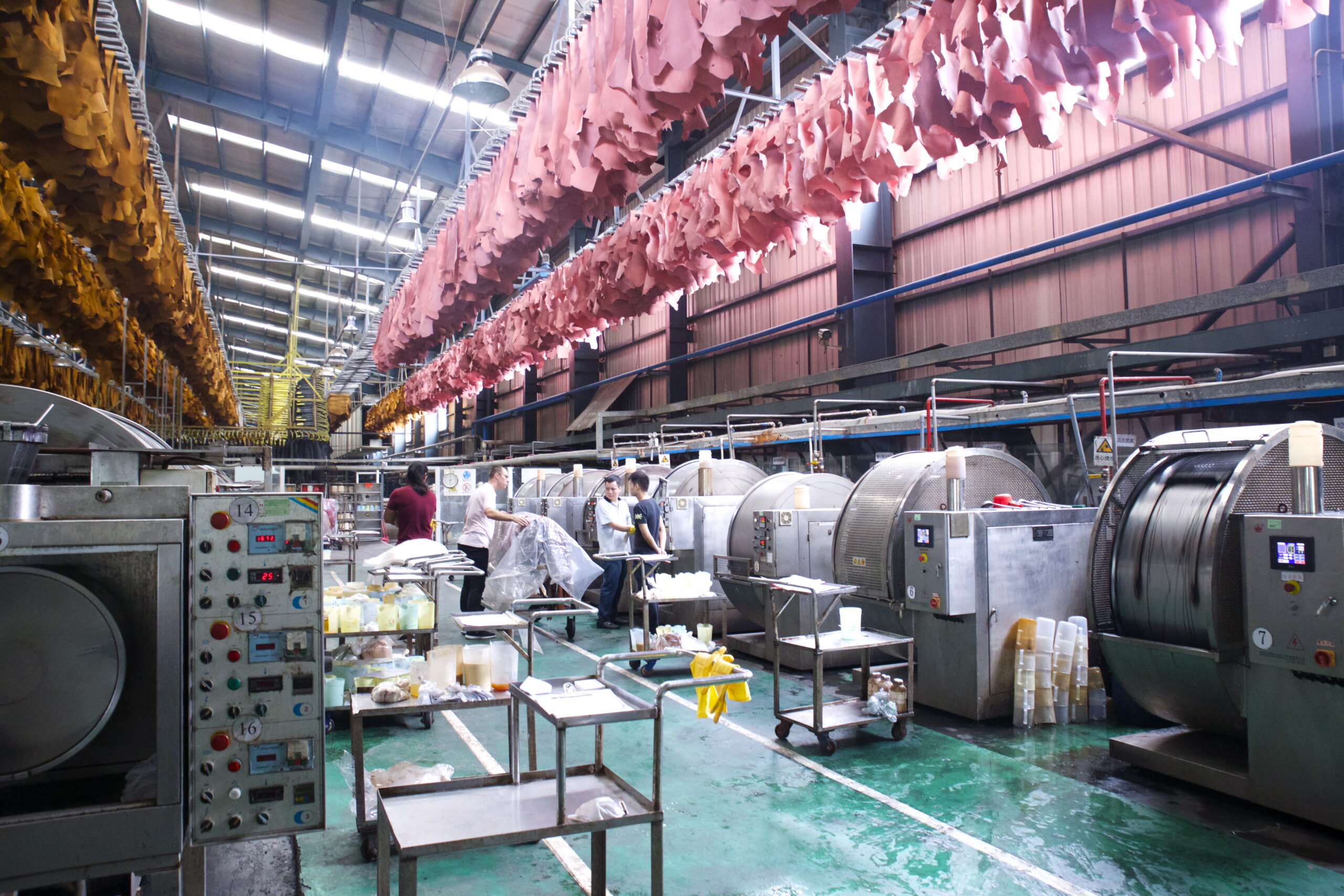

3. Modern Applications of Leather
Today, leather appreciates notoriety across different ventures, stretching out past conventional purposes. The design business, specifically, has embraced calfskin for its ageless allure and adaptability.
Fashion and Accessories: Leather jackets, handbags, and shoes remain design staples that never become unfashionable. Fashioners keep on exploring different avenues regarding leather, making creative plans that enticement for both work of art and contemporary preferences. Very good quality style houses frequently use calfskin as an image of extravagance and craftsmanship.
Furniture and Interior Design: Leather furniture stays a famous decision for its toughness and polish. Sofas, Chairs, and ottomans upholstered in leather offer solace and a bit of complexity. Leather likewise finds use in inside plan for accents like wall covers and enhancing things.
Auto Industry: In the car business, leather is inseparable from extravagance. Top of the line vehicles frequently highlight leather insides, with seats, guiding wheels, and dashboards upholstered in premium leather. This upgrades the stylish allure as well as gives solace and sturdiness.
4. The Environmental Impact of Leather
Likewise with any material, leather creation and use have natural ramifications. The leather business faces difficulties connected with manageability, squander the executives, and creature government assistance.
Sustainability: The tanning system, especially chrome tanning, can have critical ecological effects because of the synthetic compounds utilized. Endeavors are being made to foster more practical tanning techniques, like vegetable tanning and eco-accommodating other options.
Waste Management: Leather creation produces squander, including decorations and offcuts. A few organizations investigate approaches to reuse this loss into new items, lessening the by and large ecological impression.
Animal Welfare: Moral worries about creature government assistance have prompted expanded interest for elective materials, for example, vegetarian leather produced using plant-based sources. Be that as it may, many actually lean toward real leather for its exceptional characteristics.

5. The Future of Leather
The Future of leather lies in offsetting custom with advancement. As customers become more aware of ecological and moral issues, the leather business should adjust to fulfill these evolving needs.
Innovative Materials: Investigation into maintainable and moral options proceeds. Materials, for example, mushroom leather, pineapple leather, and lab-developed leather gain consideration as potential substitutes that offer comparative properties to conventional leather.
Mechanical Advances: Headways in innovation likewise impact the leather business. Computerized devices work on the accuracy and proficiency of leatherworking, while new medicines and completes improve the material’s presentation and appearance.
Consumer Trends: Purchasers today search for items that line up with their qualities. Straightforwardness in obtaining and creation, as well as an emphasis on quality and life span, are turning out to be progressively significant. Brands exhibiting a promise to these standards are probably going to flourish.

FAQ
1. What is leather?
leather is a sturdy and adaptable material made by tanning creature rawhides, basically dairy cattle stow away. It tracks down use in different items, including clothing, frill, furniture, and auto insides.
2. How is Leather made?
The leather-making process involves several steps:
- Preparation: Cleaning and getting the crude conceals eliminate hair and tissue.
- Tanning: Preserving the hides utilizing tanning specialists like vegetable tannins or chromium salts.
- Crusting: Thinning, re-tanning, and greasing up the tanned leather.
- Finishing: Coloring, Polishing, and applying a protective coating.
3. What are the various types of leather?
Several types of leather exist, including:
- Full-grain leather: The greatest, with the natural grain flawless.
- Top-grain leather: Sanded to eliminate flaws and frequently utilized for top of the line items.
- Genuine leather: Produced using the lower layers of the stow away and more reasonable.
- Bonded leather: Produced using extra leather scraps and filaments fortified together.
4. What is vegetable tanned leather?
Vegetable tanned leather uses typical tanning tracked down in plant materials, for instance, tree covering. This cycle is more innocuous to the environment than chrome tanning and results in leather with a rich, ordinary assortment that cultivates a patina after some time.
5. What is chrome tanned leather?
Chrome-tanned leather uses chromium salts in the tanning framework. This procedure is speedier than vegetable tanning and makes fragile, versatile leather that holds its shape well. It is consistently used in plan and auto undertakings.
6. How do I care for leather products?
To care for leather products:
- Keep them dry: Keep away from openness to water and moisture.
- Clean regularly: Utilize a clammy fabric for standard cleaning and a particular leather cleaner for more profound cleaning.
- Condition: Apply a leather conditioner intermittently to keep the leather delicate and forestall breaking.
- Store properly: Store leather things in a cool, dry spot away from direct daylight.
7. What are the ecological effects of leather production?
Leather creation can have gigantic normal impacts on account of the engineered materials used in tanning and the waste delivered. Be that as it may, endeavors to foster more manageable practices, for example, vegetable tanning and reusing leather squander, proceed.
8. Are there alternatives to traditional leather?
Yes, several alternatives to traditional leather exist, including:
- Vegan leather: Delivered utilizing produced materials like polyurethane or polyvinyl chloride.
- Plant-based leather: Delivered utilizing ordinary sources, for instance, pineapple leaves, mushrooms, and apple strips.
- Lab-grown leather: Made using bioengineering techniques to foster calfskin from creature cells.
9. How might I let know if a leather item is of high quality?
High-quality leather products often exhibit the following characteristics:
- Smooth and even surface: With insignificant flaws.
- Natural smell: leather has a particular, natural fragrance.
- Supple texture: Great leather is delicate and malleable.
- Consistent color: Equally colored without blotches.
- Sturdy stitching: Perfect and in any event, sewing demonstrates great craftsmanship.
10. Why is leather viewed as an luxury material?
Leather is seen as a lavishness material in view of its strength, unfading charm, and the craftsmanship drew in with its creation. Top of the line style brands and originators frequently use leather to make select and exquisite items.
11. What is the future of leather?
The eventual fate of leather includes offsetting custom with advancement. As customers become all the more ecologically cognizant, the leather business is investigating economical practices and elective materials. Progresses in innovation are additionally upgrading the quality and usefulness of leather items.
12. Can leather be recycled?
Indeed, leather can be reused. Squander leather scraps can be reused into new items, and a few organizations are creating cycles to reuse old leather merchandise into new materials. This lessens the ecological effect of leather creation.
13. How does leather compare to synthetic materials?
Leather is frequently liked for its regular feel, solidness, and capacity to foster a patina over the long haul. Engineered materials, while frequently more reasonable and accessible in a more extensive scope of varieties and surfaces, may not offer a similar life span or lavish allure as veritable leather. Nonetheless, propels in innovation are shutting the hole among manufactured and normal leather with regards to quality and maintainability.
14. What are a few normal purposes of Leather today?
leather is utilized in a wide ranges of applications, including:
- Fashion : includes leather jackets, bags, shoes, and accessories.
- Furniture : includes leather sofas, chairs, and footrests.
- Automotive : leather interiors, seats, and steering wheels.
- Sports equipment: leather gloves, leather balls, and protective gear.
- Home décor: Wall covers, cushions, and other items in development.
15. How does leather develop a patina?
Over the long run, leather develops a patina — an interesting completion that outcomes from wear and openness to components like daylight and oils from the skin. This patina adds character and magnificence to the leather, upgrading its stylish allure and making every thing remarkable.
16. What is 100 percent genuine Leather?
100% certifiable leather implies leather that is made totally from animal hide away without being mixed in with designed materials. This kind of leather holds the normal properties of the stow away, offering strength, breathability, and the capacity to foster a patina.
17. Why is leather used?
Leather is used for its durability, versatility, and ever-enduring elegant appeal. It is similarly impenetrable to mileage, making it ideal for a large number of things, from plan to furniture.
18. What animals is leather from?
Leather can be produced using the stows away of different creatures, including cows, sheep, goats, pigs, and colorful creatures like gators, snakes, and ostriches. Each sort of Leather has exceptional characteristics that suit various applications.
Conclusion
Leather’s helping through bid lies in its extraordinary blend of greatness, robustness, and adaptability. From its old beginning stages to its state of the art applications, leather continues to be a material of choice for individuals who regard quality and craftsmanship. As the business creates to address regular and moral hardships, leather’s future looks empowering, with imaginative plans preparing for a more viable and trustworthy method for managing this interminable material.


Pingback: What is PU Leather? Understanding the Popular Synthetic Material